Written by Ypatios Moysiadis, Managing Partner at Wattcrop.
In an age where every kilowatt counts and every byte leaves a footprint, the convergence of blockchain and energy is not just a technical evolution—it’s a deeply human response to some of the most pressing challenges of our time. From the streets of Punggol to the fjords of Scandinavia, communities, innovators, and policymakers are turning to blockchain not as a buzzword, but as a backbone for a more just and sustainable energy future.
What began as a decentralized financial experiment now powers initiatives that put agency back in the hands of individuals and small producers, rewards conscious consumption, and redefines what energy independence can look like. As 2025 unfolds, blockchain is no longer a fringe technology—it’s a trusted tool driving transparency, equity, and global cooperation in the energy sector.
A Booming Market: Forecasts and Drivers
The numbers tell a compelling story. The global blockchain-in-energy market reached a value of $3.1 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a staggering compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41.6%, reaching $90.8 billion by 2034. This isn’t just market speculation—it’s a reflection of deep structural shifts:
- Growing demand for decentralized, renewable, and democratized energy.
- Global mandates to reduce carbon footprints and track emissions with integrity.
- Smart contract, AI, and grid automation technologies maturing in tandem.
- A philosophical and technical shift from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake—reducing energy waste while boosting efficiency.
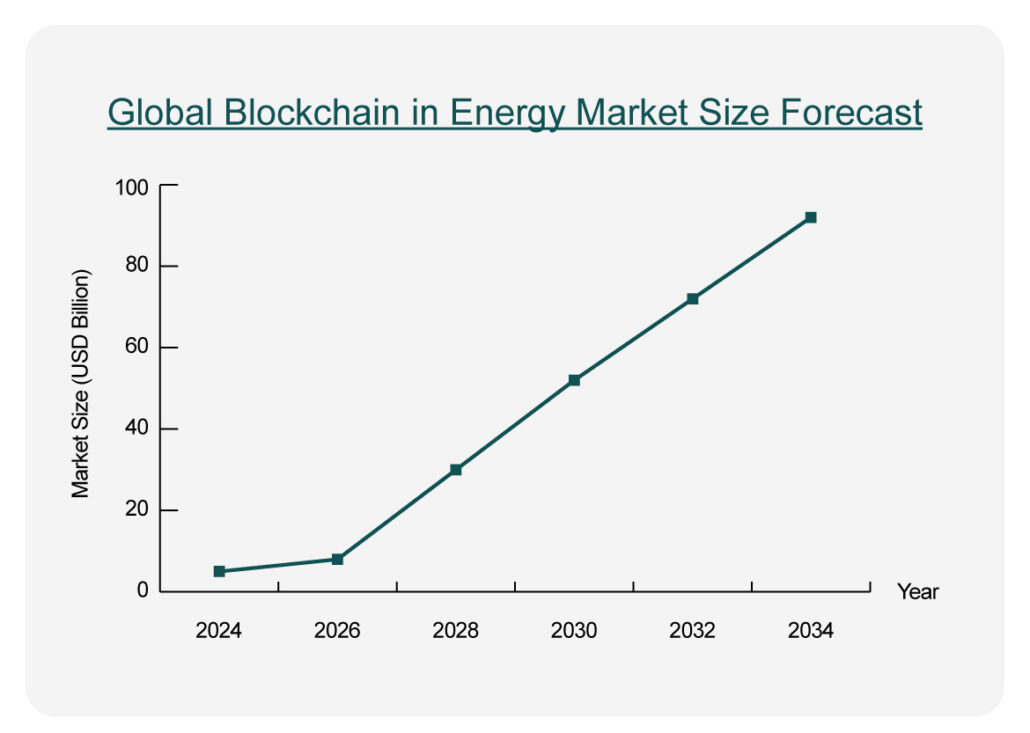
Figure 1. Forecast of the Global Blockchain-in-Energy Market (2024–2034)
Trends Reshaping the Energy Sector
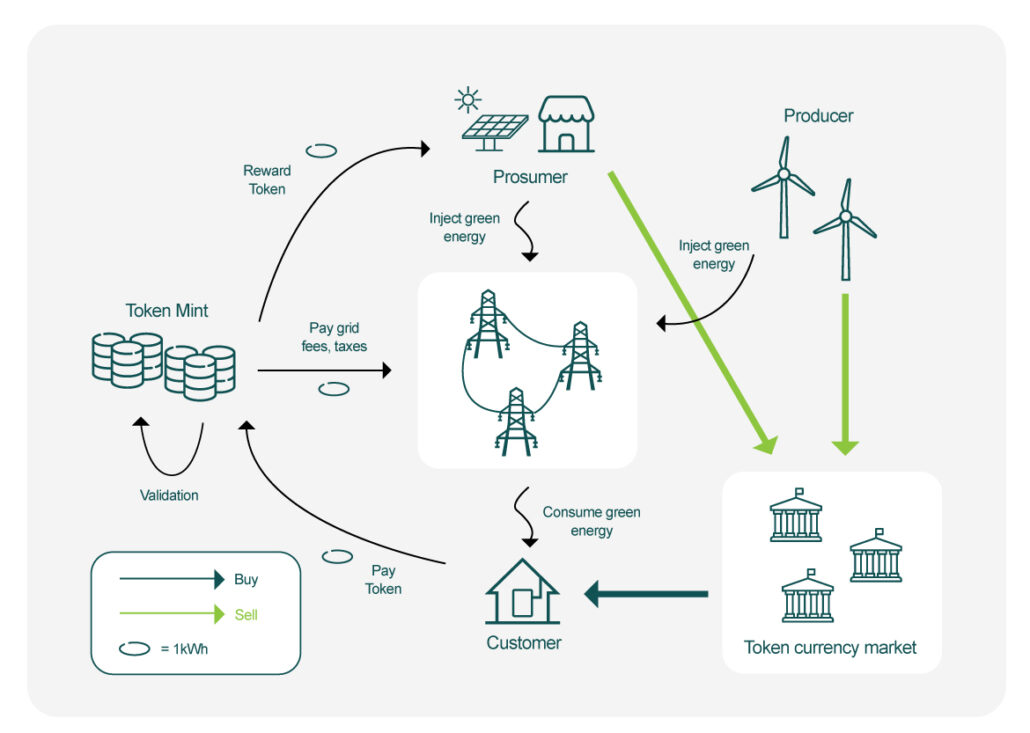
- Decentralized Energy Trading
Energy is no longer the sole domain of massive utilities. Blockchain enables peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading where neighbors can buy and sell power from each other. The result? Local resilience, lower costs, and community empowerment.
- Tokenization of Carbon Credits
In an era of greenwashing, blockchain brings verifiable integrity. Tokenized carbon credits mean emissions reductions are no longer vague claims but traceable assets.
- AI-Blockchain Integration
Smart contracts and AI algorithms are working together to forecast consumption, detect faults, and automatically rebalance supply and demand in milliseconds. The grid is not just smarter—it’s becoming sentient.
- Shift to Sustainable Protocols
When Ethereum transitioned to PoS, it didn’t just reduce emissions—it set a standard. Now, PoW-based systems face growing pressure to evolve or face regulation.
- Regulatory Momentum
From Singapore’s innovation grants to the UN’s mining levy proposal, governments are moving quickly to either embrace or regulate blockchain’s energy impact. And increasingly, the line between the two is blurring.
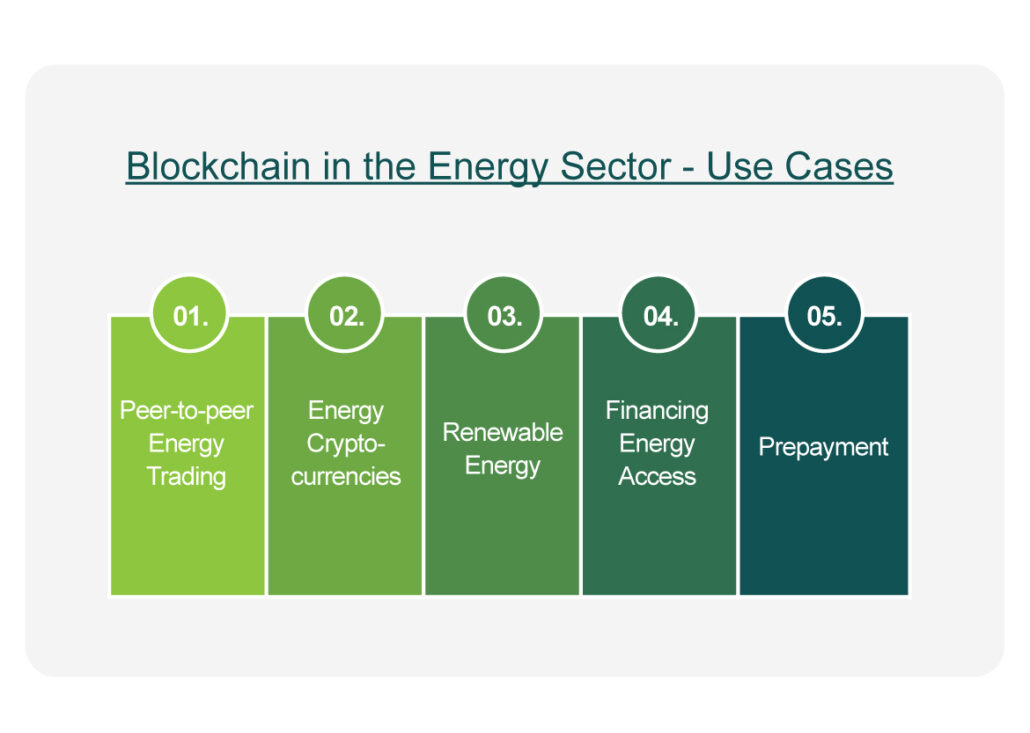
Key Use Cases in 2025
Real-world applications are the heartbeat of blockchain’s energy revolution:
- P2P Energy Trading: Families selling solar energy directly to their neighbors.
- Carbon Credit Tokenization: Farmers and startups monetizing verified carbon capture.
- Green Crypto Mining: Developing nations turning excess renewable power into digital gold.
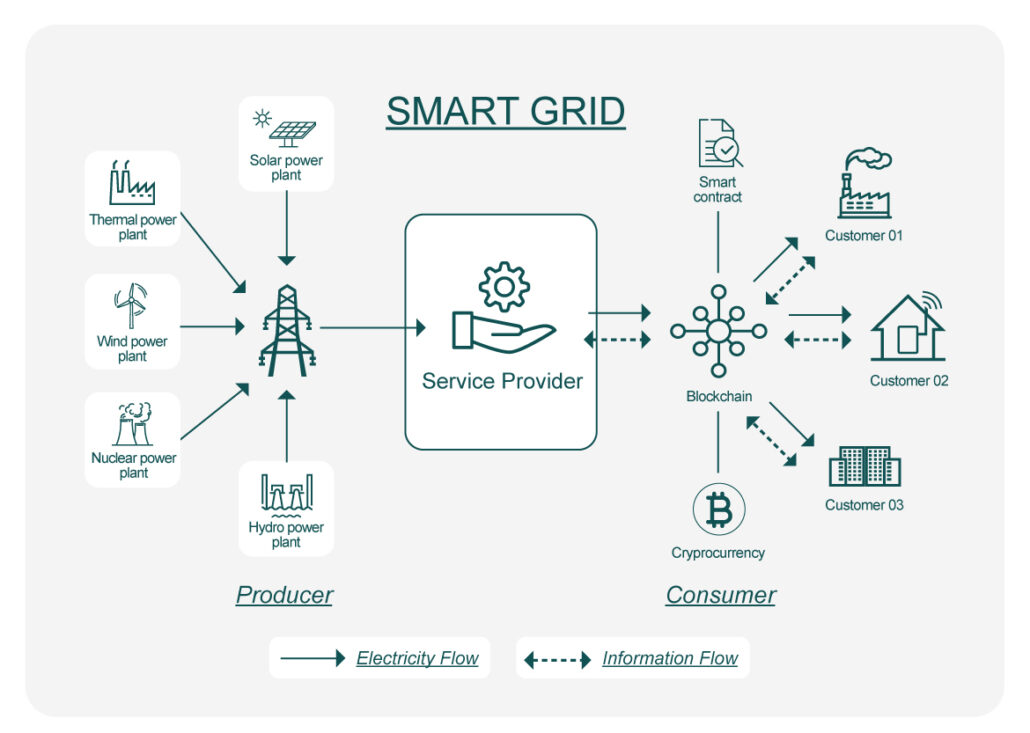
- Smart Grid Automation: Sensors and code keeping lights on in ways humans alone never could.
- Tokenized Energy Assets: Micro-investments into solar farms from mobile apps.
- Lifecycle Tracking: Following batteries from cradle to grave to boost recycling and reduce waste.
Additional Charts & Quantitative Data
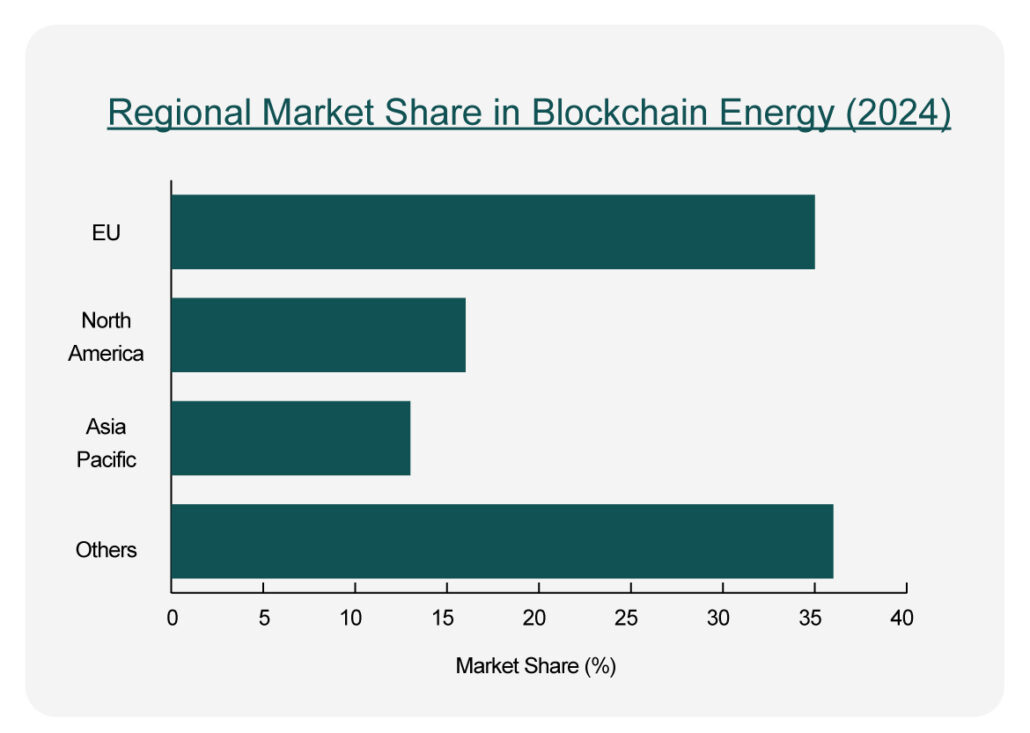
- Regional Market Share in Blockchain-Energy (2024)
Europe leads with over 35% market share (~USD 1.94 bn), followed by North America (~16%) and Asia–Pacific. Private blockchains dominate (~65%), and energy trading platforms account for ~30% in applications.
- U.S. Blockchain-in-Energy Market Growth
U.S. market grew from USD 160 mn in 2022 → USD 200 mn in 2023 → USD 260 mn in 2024. North America held ~15.8% of global blockchain-energy share in 2024.
- Global Market Size & CAGR Variances
- Global valuation of USD 3.1 bn in 2024, expected CAGR of 41.6% to USD 90.8 bn by 2034.
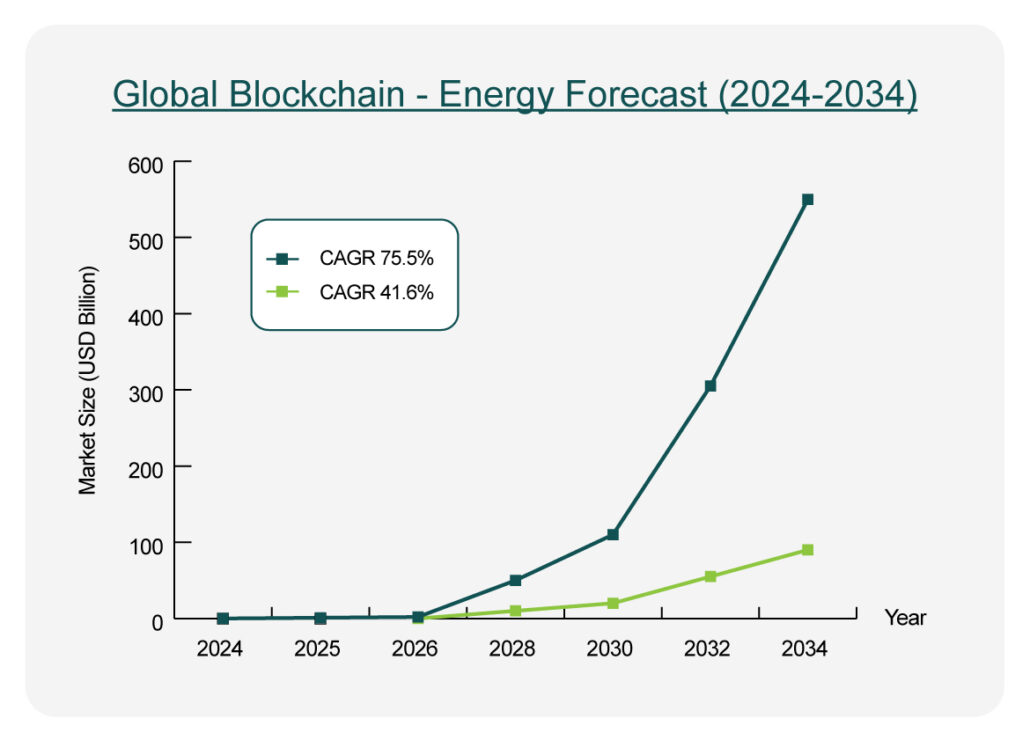
- Alternate forecast shows explosive growth from USD 3.5 bn in 2025 → ~USD 548 bn by 2034 (CAGR ~75.5%)—highlighting diverging projections depending on scope and definition.
Expanded Regional Case Studies
Singapore – P2P Renewable Trading & Smart Grids
In the heart of Southeast Asia, Singapore has become a living lab for clean energy tech. The national IES system and PacificLight grid allow real-time electricity pricing and exchange. Senoko Energy’s peer-to-peer trial is not just a tech demo—it’s a story of how city-dwellers can reclaim energy autonomy.
European Union – Regulatory Framework & Investment
Across Europe, blockchain is being woven into climate law. The EU’s “Fit for 55” package, backed by €584 bn in projected investment, requires radical transparency in emissions. A green label for blockchain itself is in the works—making the medium as clean as the message.
United States – Pilot Projects & Funding
In labs and communities from California to Colorado, the U.S. is testing blockchain for everything from solar billing to electric vehicle charging. With over 110 pilot programs, the groundwork is being laid for an energy system that is both decentralized and national.
Interpretation & Insights
- Europe: The leadership position is fueled by proactive policy, massive investment, and first-mover advantage in blockchain-based energy and emissions transparency.
- Singapore/Asia–Pacific: A high-tech frontier in P2P renewable trading and smart grid deployment, leveraging integrated infrastructure and regional collaborations.
- North America: Rapid but measured growth, supported by government R&D funding and emerging pilot deployments—positioning it alongside Europe.
- Forecast Divergence: The contrast between 42% CAGR and 75% CAGR underscores the nascency of this sector; actual adoption may reflect evolving definitions (BaaS, carbon markets, etc.).
Regulatory and Policy Landscape
- UN Crypto Mining Tax: $0.045/kWh proposed levy aims to shift incentives toward green blockchains.
- EU Initiatives: Climate laws are mandating emissions traceability via blockchain.
- Asia-Pacific Leadership: Governments fund next-gen grid pilots and IoT-blockchain hybrids.
- U.S. DOE Support: Public money is enabling proof-of-concept projects to scale.
These policies reflect more than strategy—they signal a global shift toward holding digital infrastructure accountable for its physical impact.
Technological Convergence
AI and blockchain are forming a potent combination. Predictive algorithms enhance energy management by forecasting load, identifying faults, and adjusting supply—all powered by smart contracts and distributed ledgers. Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake (PoS) and the emergence of low-energy consensus protocols like DAG (Directed Acyclic Graphs) are enabling high-throughput, low-energy blockchain infrastructures.
In-Depth Analysis: Top 10 Blockchain-Energy Initiatives
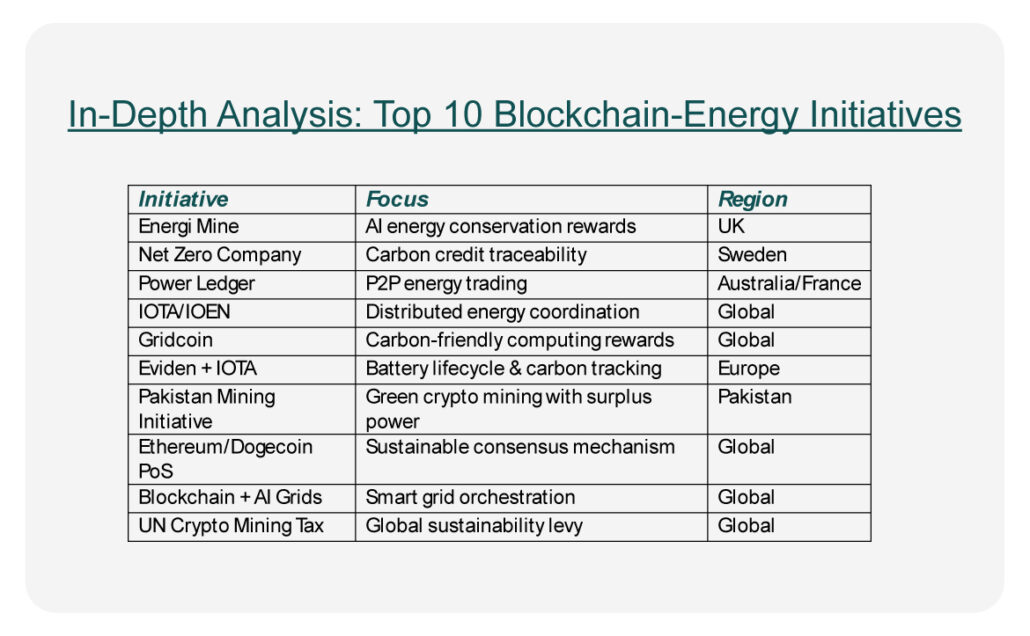
- Energi Mine (United Kingdom)
Energi Mine incentivizes energy-efficient behavior through blockchain-powered rewards. Consumers and businesses earn ETK tokens for reducing energy consumption, which can then be spent on energy services, transport, or traded. The project is rooted in behavioral science, encouraging a culture of sustainability in both homes and industries.
- Net Zero Company (Sweden)
This initiative issues tokenized carbon credits linked to real-world carbon capture, ensuring traceability and transparency. Each token represents one verified ton of CO₂ offset. Sweden’s strong environmental governance supports the initiative’s credibility, offering a model for decentralized, honest carbon accounting.
- Power Ledger (Australia/France)
One of the pioneers in energy blockchain, Power Ledger enables P2P energy trading, allowing individuals and communities to trade surplus solar energy. Operating in various regulatory sandboxes, including France and Australia, it has helped decentralize energy markets while validating the reliability of blockchain-based settlement.
- IOTA/IOEN (Global)
IOTA’s unique architecture—using a directed acyclic graph (DAG)—eliminates transaction fees, making it ideal for energy micro-transactions. IOEN (Internet of Energy Network), built on IOTA, connects local grids globally, creating digital energy communities that optimize energy distribution and use through intelligent contracts and IoT sensors.
- Gridcoin (Global)
Gridcoin rewards users for contributing computing power to scientific research through the BOINC platform. Using a PoS protocol, it showcases how blockchain can support not only low-energy validation but also socially beneficial computation. It’s a niche but powerful use case for aligning blockchain with sustainability and science.
- Eviden + IOTA (Europe)
This partnership focuses on the traceability of energy-intensive components like batteries across their lifecycle. By recording origin, usage, recycling, and disposal, this system supports a circular economy while ensuring compliance with upcoming EU environmental reporting standards. It’s blockchain used as a truth machine for green compliance.
- Pakistan Mining Initiative
Pakistan is capitalizing on surplus renewable energy, especially hydropower, by inviting miners to set up sustainable operations. The initiative provides a use for otherwise wasted energy and creates an economic incentive to expand renewable infrastructure. It demonstrates how blockchain mining, often maligned for energy use, can instead promote clean development.
- Ethereum & Dogecoin PoS Migration (Global)
The switch from PoW to PoS in Ethereum—and more recently Dogecoin—represents one of the most impactful energy-reduction moves in the crypto space. Ethereum’s shift alone has reduced its energy consumption by over 99.9%. These migrations set industry precedents and challenge other projects to follow suit or face regulatory and social pressure.
- Blockchain + AI Smart Grids (Global)
Combining blockchain with AI enables real-time grid management, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making. These systems can anticipate faults, reroute power, and ensure grid stability with minimal human intervention. Projects in Europe, Japan, and the U.S. are leading pilots to prove their effectiveness at scale.
- UN Crypto Mining Tax Proposal (Global)
The United Nations’ proposed tax on energy-intensive crypto mining seeks to fund global sustainability initiatives. At $0.045/kWh, it aims to redirect capital from high-carbon mining to green alternatives. While still in proposal form, it reflects increasing geopolitical momentum to hold digital systems accountable for physical-world emissions.
From Carbon Credits to Smart Grids
Initiatives like Sweden’s Net Zero Company and Australia’s Power Ledger are leading the charge in applying blockchain to carbon accountability and local trading. Pakistan is leveraging its surplus renewable capacity to host green crypto mining farms, while the United Nations proposes levies on high-energy mining to redirect funds into climate action.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Blockchain’s rise in energy is not without its growing pains. Interoperability with existing infrastructure, scale limits, and public understanding still lag behind the tech. But with collaboration and investment, these gaps are narrowing.
Conclusion: From Disruption to Infrastructure
Blockchain’s role in the energy sector is not just technical—it’s profoundly human. It’s about trust, equity, and empowerment in a world seeking balance. With a current valuation of $3.1 billion and projections soaring beyond $90 billion, this space isn’t just growing—it’s maturing.
Investors, governments, and grassroots communities are co-authoring a future where energy is cleaner, smarter, and more shared. Blockchain is not a silver bullet—but it is a powerful scaffold on which the next generation of energy systems will be built.
For every entrepreneur with a solar panel, every regulator balancing innovation and safety, and every citizen with a conscience—this revolution belongs to all of us.