Written by Elena Gkagkani, head of strategy and development at Wattcrop.
Introduction:
In the quest for a sustainable future, hydrogen has emerged as a game-changer. As the most abundant element in the universe, hydrogen presents a vast source of clean fuel with immense potential. Governments, investors, and industry leaders worldwide are increasingly recognizing the role of hydrogen in decarbonization efforts. With over 1,000 hydrogen projects underway globally, and more than 350 announced in the past year alone, the momentum for green hydrogen is undeniable. This article explores the driving forces behind the green hydrogen revolution and the challenges that lie ahead.

Unlocking the Potential of Green Hydrogen:
Hydrogen’s potential as a clean fuel stems from its ability to produce energy with minimal environmental impact. Unlike fossil fuels, hydrogen combustion only releases water vapor as a byproduct, making it a truly zero-emission fuel. Furthermore, hydrogen can be produced through various methods, including electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. This process yields “green hydrogen,” which has no carbon emissions throughout its production cycle.
Global Investments and Market Trends:
The growing interest in hydrogen is evident in the substantial investments being made in the sector. Beyond venture capitalists and buy-out firms, governments are also actively supporting hydrogen initiatives. For instance, the European Union’s Green Deal and the United States’ Clean Energy Innovation Program allocate significant funding to hydrogen research, development, and infrastructure. Additionally, public markets have witnessed a surge in hydrogen-related investments, with companies like Plug Power capturing investors’ attention.
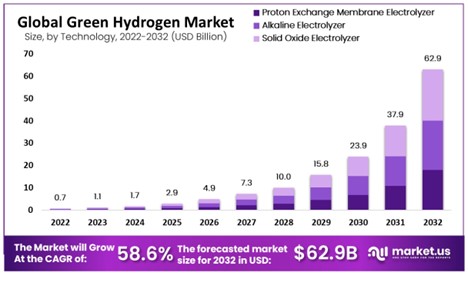
Overcoming Challenges for Green Hydrogen Adoption:
While the industry faces challenges such as rising capital costs, sourcing critical minerals, and securing renewable power supply, there is growing optimism that these hurdles can be overcome. As the industry matures, the costs of producing green hydrogen are expected to decrease. McKinsey predicts that by 2030, a kilogram of green or blue hydrogen can be produced for $2.50 to $3.50 without subsidies, making it increasingly competitive with hydrogen derived from natural gas.
Currently, green hydrogen production is relatively expensive compared to hydrogen derived from fossil fuels. However, as technology advances and economies of scale kick in, the costs are expected to decline significantly. Collaborative research and development efforts are focused on improving electrolysis efficiency, exploring alternative catalysts, and reducing the capital costs associated with hydrogen infrastructure.
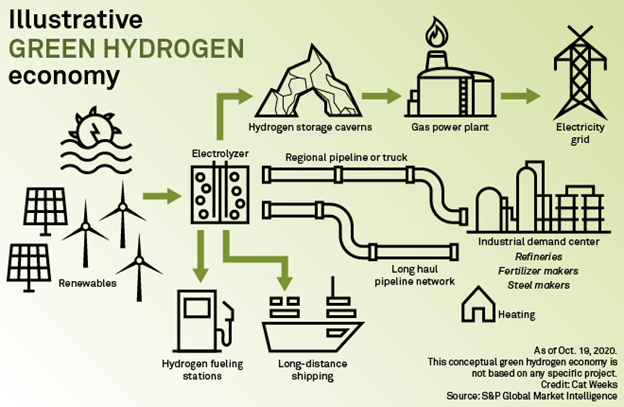
Building Infrastructure and Scaling Production:
A crucial aspect of the green hydrogen revolution is the development of a robust infrastructure. The establishment of hydrogen production facilities, storage systems, and distribution networks is essential to enable widespread adoption. Countries like Germany, Japan, and Australia are at the forefront of building hydrogen infrastructure, investing in hydrogen hubs, and creating dedicated hydrogen corridors. These efforts aim to create a self-sustaining hydrogen ecosystem capable of supplying various sectors, from transportation to industrial applications.
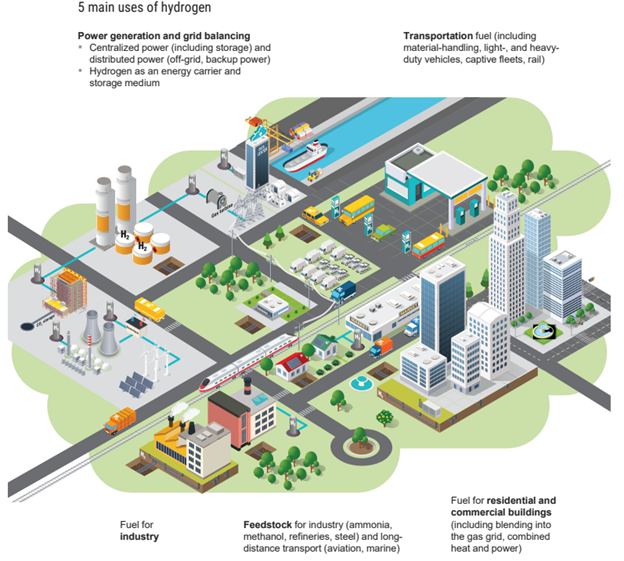
Hydrogen Applications and Sector Integration:
Green hydrogen has the potential to decarbonize a wide range of industries. Sectors such as heavy-duty transportation, shipping, aviation, and industrial processes that are challenging to electrify can benefit greatly from hydrogen utilization. For example, fuel cells powered by hydrogen offer a viable solution for long-haul trucks, where battery-powered electric vehicles face limitations in terms of range and payload capacity. Integrating green hydrogen with renewable energy systems can also provide long-term energy storage capabilities, balancing intermittent renewable energy generation.
Government Support and Policy Frameworks:
Governments play a vital role in shaping the hydrogen landscape through policy support and regulatory frameworks. Many countries have already formulated hydrogen strategies and are implementing supportive measures to stimulate investment and create market demand. These measures include financial incentives, grants, tax credits, and regulations that encourage hydrogen adoption. Furthermore, international collaborations and partnerships facilitate knowledge sharing and foster a global hydrogen economy.
Conclusion:
The green hydrogen revolution is well underway, driven by increasing investments, technological advancements, and favorable policy environments. While challenges remain, the immense potential of green hydrogen as a clean and versatile fuel cannot be ignored. As governments, industry leaders, and investors continue to collaborate and innovate, the transition to a hydrogen-powered future becomes increasingly feasible. By harnessing the power of green hydrogen, we can accelerate the shift towards a sustainable and decarbonized world, fueling a green revolution that benefits both the environment and future generations.
Sources: McKinsey, The Economist, DBS Bank, Fuel Cell & Hydrogen Energy Association (FCHEA), globenewswire, market.us, S&P Global

