Written by Riki Argyropoulou, junior surveyor at Wattcrop.
In the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, the concept of microgrids has emerged as a pioneering strategy, particularly for remote and vulnerable communities. These communities, often located in rural areas or on islands, face unique challenges in accessing reliable and affordable electricity due to their geographical isolation and reliance on centralized power grids. However, renewable energy microgrids offer a promising solution, providing a decentralized, resilient, and sustainable source of electricity tailored to the specific needs of these communities.
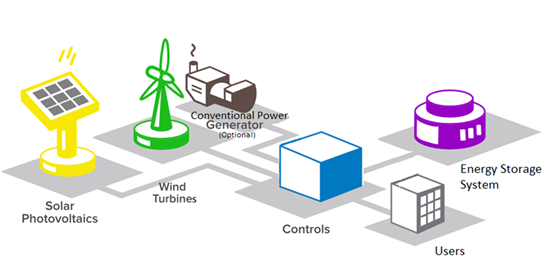
Renewable energy microgrids are localized power systems that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, utilizing a combination of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and storage technologies. Unlike traditional centralized power grids, which are vulnerable to disruptions and outages, microgrids offer increased reliability and resilience by diversifying energy sources and enabling islanding capabilities, allowing them to continue operating autonomously during grid outages or emergencies.
Renewable energy microgrids benefits:
For remote communities, particularly those located in areas with limited access to reliable electricity infrastructure, renewable energy microgrids provide a lifeline for essential services such as healthcare facilities, schools, and telecommunications. By harnessing abundant renewable resources available in their surroundings, these communities can reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, mitigate energy costs, and improve energy security and self-sufficiency.
Moreover, renewable energy microgrids offer environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change. In remote and vulnerable regions where diesel generators or other fossil fuel-based power systems are often used, transitioning to renewable energy microgrids can significantly decrease carbon emissions and air pollution, leading to improved health outcomes and environmental sustainability.
One notable example of the transformative potential of renewable energy microgrids is the island nation of Puerto Rico. In the aftermath of Hurricane Maria in 2017, which devastated the island’s centralized power grid, communities across Puerto Rico faced prolonged power outages and infrastructure damage. In response, organizations and communities collaborated to deploy renewable energy microgrids powered by solar panels and battery storage systems, providing reliable electricity to critical facilities and communities, even during grid disruptions.
Similarly, in remote indigenous communities around the world, renewable energy microgrids have enabled access to electricity for the first time, catalyzing economic development, improving living standards, and preserving cultural heritage. By incorporating local knowledge and community engagement into the design and implementation process, renewable energy microgrids can be tailored to meet the unique needs and priorities of each community, fostering ownership and sustainability.
Challenges:
Despite their numerous benefits, the widespread adoption of renewable energy microgrids still faces challenges, including upfront costs, technical complexities, and regulatory barriers. However, advancements in renewable energy technologies, coupled with supportive policies and financing mechanisms, are increasingly making microgrid solutions more accessible and cost-effective.
As we continue to confront the urgent challenges of climate change and energy access, renewable energy microgrids represent a pioneering solution for empowering remote and vulnerable communities. By harnessing the abundant resources of nature and leveraging innovative technologies, we can build resilient, sustainable, and inclusive energy systems that ensure no community is left behind in the transition to a cleaner
Read more interesting news from the Wattcrop team!
Learn everything about renewable energy and sustainability!

